
The 39th Annual meeting of RSSDI (Research Society for the Study of Diabetes in India) was held from 4th to 6th November, 2011 at Mumbai.
The research team from MVH won awards for various presentations. The excerpts are elaborated below.
1. Topic: Association of HSPA1B gene polymorphism in T2DM and its Complications: A South Asian Study.
Dhamodharan U, Ezhilarasi K, Parthiban M, Indira Padmalayam, Rama Rajaram, Vijay Viswanathan
Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Genetics, Prof. M.Viswanathan Diabetes Research Centre & M.V. Hospital for Diabetes in collaboraton with Department of Biochemistry & Biomaterials, Central Leather Research Institute , Adyar, Chennai.
Heat Shock Protein-70 (HSP70) a protein which is very active in the immune system is suppressed in people with diabetes because of cellular stress. Western studies have reported the association of this gene (HSP70) in diabetic individuals through its effect on insulin sensitivity.
Our researchers studied this effect on T2DM and its complications among South Indian population and have found the mutation of this gene in T2DM and in those with both micro- and macro vascular complications.
Thus this novel gene could be used as a marker to identify people with increased risk of diabetes and its complications and take preventive action at an early stage.
2. Topic: Stress Response Element (STRE) single nucleotide polymorphism in Lipoic acid Synthase gene is associated with T2DM with complications.
Ezhilarasi K, Dhamodharan U, Parthiban M, Indira Padmalayam, Rama Rajaram, Vijay Viswanathan
Department of Biochemistry & Molecular Genetics, Prof. M.Viswanathan Diabetes Research Centre & M.V. Hospital for Diabetes in collaboraton with Department of Biochemistry & Biomaterials, Central Leather Research Institute , Adyar, Chennai.
STRE in the LASY promoter region is important for the synthesis of Lipoic Acid Synthase gene which produces Lipoic Acid that acts as an antioxidant. Under normal conditions, Stress Response Element binds to STRE site and helps in the production of antioxidant enzymes such as Catalase LASY which helps to control oxidative stress.
Our researchers have found that in the case of T2DM with complications- neuropathy, nephropathy or retinopathy, this enzyme production is reduced due to single nucleotide polymorphism.
This provides great scope for further investigation into the use of this information in treating complications of diabetes. 
3. Topic: Chennai Slim & Fit poster presentation.
Dr. Vigneswari, Research Assistant, Department of Epidemiology.
Childhood obesity has emerged as a major public health issue in India. These children are at high risk of developing diabetes, CVD earlier in their life compared to their normal counterparts.
As a school based approach, M.V Hospital for Diabetes and Prof. M. Viswanathan Diabetes Research Centre conducted an awareness creation programme (Chennai Slim and Fit) on childhood obesity in 13 CBSE schools with audiovisual aids and provided them with a chance for direct interaction with health experts. More than 20,000 children were benefited through this programme. It was highly successful, as the pre- and post- knowledge assessment showed that there was a significant increase in the degree of awareness among the children who participated in the programme.
The team from MVH at RSSDI- 2011. (L to R Mr.Dhamodharan Umapathy, Dr.K.Satyavani, Dr.Hemanga Barman, Prof.Vijay Viswanathan, Dr.M.Parthiban, Ms.K.Ezhilarasi, Mrs.R.Seena, Ms.Vimala, Dr.Vigneswari)
Welcome to M.V Hospital for Diabetes, established by late Prof. M.Viswanathan, Doyen of Diabetology in India in 1954 as a general hospital. In 1971 it became a hospital exclusively for Diabetes care. It has, at present,100 beds for the treatment of diabetes and its complications.
Saturday, December 31, 2011
MVH wins laurels for paper presentation at RSSDI – 2011
|
Bookmark this post:
|
|
Wednesday, December 14, 2011
Cervical Spondylosis in Diabetes
S.Bamila
M.V. Centre for Diabetic Foot Care, Podiatry, Research & Management
Cervical spondylosis is a common cause of chronic neck pain. It occurs when there is abnormal wear on the cartilage and bones of the neck (cervical vertebrae).
The most common cause is ageing. By 60 years, most women and men show signs of cervical spondylosis.
Other factors that can cause spondylosis are:
* Not exercising and being overweight
* Lifting heavy weights or a lot of bending and twisting
* Previous neck injury (often several years before)
* Earlier spine surgery
* Ruptured or slipped disc
* Severe arthritis
* Small fractures to the spine due to osteoporosis
* Diabetes
* Faulty posture:
-slouching or sitting incorrectly on soft chairs and couches
- bad back and neck posture from sleeping on a soft mattress
- lifting weights incorrectly
* Malnutrition
* Stress and strain from sitting for a long time
* Emotional problems leading to muscle cramping
Symptoms
* Severe nagging pain spreading to both the sides of the shoulders, back of the neck, the collar bone and head. Pain in arms and fingers. At times, chest and throat too could be affected.
* Acute or chronic stiffness, leading to partial or complete loss of movement.
* Numbness and tingling or complete loss of sensation on the affected side.
* Headache
* Giddiness
* Weakness of muscles in the arm or hand.
* Loss of balance (less common)
* Loss of control over the bladder or bowels (if there is pressure on the spinal cord)
Treatment
Most symptoms respond to basic treatment such as:
* Rest - This may range from reducing normal activities to complete bed rest for three to five days.
* Neck collar or brace - this restricts neck movement so that the shoulders take the weight of the head.
* Traction - in some cases intermittent neck traction may be recommended for one to two weeks. This may be done in the hospital or at home.
* Pain relieving drugs /Pain-relieving injections
* Physical therapy /yoga work on improving posture. In cases of severe or chronic pain or loss of movement, surgery may be recommended.
* Chronic neck pain is also sometimes associated with anxiety and depression which may also need to be treated.
Exercises for Neck Pain and Spondylosis
Here are basic stretches and exercises that can be used by almost everyone in pain. However, always consult your doctor before beginning an exercise plan.
Exercise for 10-15 minutes a day. Do the entire routine for maximum relief.
1.Extension and flexion is especially helpful for stiff back and neck.
Flexion
Lower your head and bring it forward so that the chin touches the chest and your face is staring straight down at the floor. Do this slowly five times.

You can also add gentle pressure by putting your hands behind your head to hold the end position.
Extension
Allow the head to go back until you look directly at the ceiling.
Caution: Don’t do this movement fast or forcefully as it forces all the small joints at the back of the neck into an extreme position. 
2. Rotation
Turn your head slowly round to one side until it cannot easily go any further.
Caution: Do not go from one side to the other in the individual movements or roll your neck about.
Hold your neck at the end of the movement for a few seconds. Do this five times to one side and then repeat on the other side.
Don’t do this if you feel dizzy. Dizziness, especially in older people, might mean that the blood vessels in your neck are being squeezed by the position.
3.Side Bend
Side bends increase your side-to-side flexibility. Start by lacing your fingers together and pointing your elbows outward. Bend at the waist, tilting your body to one side as far as you can. Then bend your head and neck in the same direction. Repeat on your other side. Repeat this exercise 10 times.
4. Sit And Twist
This exercise increases the flexibility of your entire spine. To begin, lace your fingers together and point your elbows outward. Slowly and gently twist at your waist, rotating your head and neck to the same side. Repeat toward the other side. Repeat this exercise 10 times.
5. Side / Lateral flexions (Tilt)
Facing forward try and tip your ear down towards the same shoulder.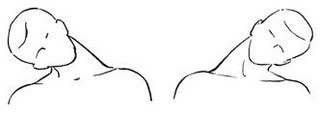
6. Strengthening exercise.
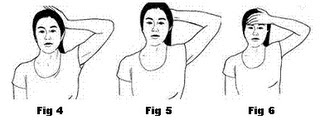
Reach your right arm over your head so that your palm is on top of your skull, your fingers resting just above the left ear. Allow the weight of your arm, along with light fingertip pressure, to gently bend the head toward your right shoulder (fig.1). Check to make sure your shoulders are still relaxed. You should be looking forward. Hold the pose for 30 seconds.
Move your fingers toward the back left corner of your skull, this time allowing your head to bend forward and to the right, about 45 degrees in front of your shoulder (fig.2). Hold for 30 seconds.
Now place your fingers at the back of your skull and gently pull your head straight forward, toward your chest (fig.3). Hold for 30 seconds. Switch hands and repeat the stretches in reverse order: Pull forward, then 45 degrees in front of your left shoulder, and finally directly over your left shoulder. Do not push your head backward.
Place your hand against the side of your head. Try to bring to your ear to your shoulder, resisting the motion. Repeat this exercise on the other side. Hold each position for 5 seconds and when finished relax slowly. Repeat this exercise on the other side. Hold each position for 5 seconds and when finished relax slowly. Repeat with your right hand on the right side of the head. Do the same exercise, using either hand, with the back of the head (fig.5) and the forehead (fig.6)

Preventing Cervical Spondylosis
* Exercise regularly and don’t engage in activities that place pressure on the head, neck, and shoulders.
* Low-impact activities, such as swimming, walking, or yoga are ideal for the health of the cervical spine.
* Maintain good posture while standing, sitting, working at the computer, driving and sleeping.
* Do not hold the head in the same position for long periods. Take regular breaks when driving, watching TV or working on a computer.
*Use a seat belt in a car and avoid activities that strain the neck to protect the neck from injury.
*Avoid bending forward suddenly.
*Avoid nodding head movements.
*Make lifestyle modifications.
REFERENCE:
1. http://cervicalspondylosis.com/exercises_for_cervical_spondylosis.htm
2. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmedhealth/PMH0001472
3. http://www.patient.co.uk/health/CervicalSpondylosis.htm
|
Bookmark this post:
|
|
Monday, December 5, 2011
Carpal Tunnel Syndrome in Diabetes
S.Bamila
M.V. Centre for Diabetic Foot Care, Podiatry, Research & Management
Diabetes, alcoholism and obesity are medical problems that are associated with carpal tunnel syndrome
This is also common among people who perform repetitive motions of the hand and wrist. Typing on a computer keyboard is probably the most common cause of carpal tunnel syndrome. Other causes include sewing, driving, writing, playing some musical instruments, painting and so on.
The median nerve in the wrist supplies feeling and movement to parts of the hand. The area in your wrist where the nerve enters the hand is called the carpal tunnel. Carpal tunnel syndrome is pressure on the median nerve, and this can lead to numbness, tingling, weakness, or muscle damage in the hand and fingers. The condition occurs most often in people between 30 and 60 years, and is more common in women than in men. It also has a higher prevalence in people with diabetes and other conditions which directly affect the nervous system.
What causes Carpal Tunnel Syndrome?
* Doing the same action over and over again
* Uncomfortable joint posture
* High force
* Vibration
* Direct pressure
* Uncomfortable posture for a long time
Symptoms
* Numbness or tingling sensation in the thumb and the next two or three fingers of one or both hands
* Numbness or tingling sensation in the palm
* Pain spreading right up to the elbow
* Pain in the wrist or hand/s
* Problems with fine muscle coordination in one or both hands
* Wasting away of the muscle under the thumb (in advanced or long-term cases)
* Weak grip or difficulty in carrying heavy things like bags (a common complaint)
* Weakness in one or both hands
* Interruption of sleep with numbness and in pain in hands
* Poor circulation of blood in hands resulting in a temporary lack of sensation
* Cold hands
* Dropping objects especially small things.
* Loss of Grip Strength by Fore arms
Signs and Tests
Untreated CTS
* Numbness in the palm, thumb, index finger, middle finger, and thumb side of the ring finger
* Weak hand grip
* Tapping over the median nerve at the wrist may cause pain to shoot from the wrist to the hand (this is called Tinel's sign)
* Bending the wrist forward all the way for 60 seconds will usually result in numbness, tingling, or weakness (this is called Phalen's test)
* Electromyography
* Nerve conduction velocity
* Wrist X-rays should be done to rule out other problems like wrist arthritis
* MRI scan, ultrasound imaging
Using wrist splint at night or during sport activities, high-frequency sound waves directed toward the inflamed area , alternating warm and cold soaks, restricted movement, Vitamin B6 and acupuncture are some forms of treating this. Some stretching exercises can be done to prevent re-occurrence.
* Stretching exercises for Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
Pull forward and stretch both wrists and fingers as if they are in a hand-stand position. Hold for a count of 5. 
Straighten both wrists and relax fingers.
Make a tight fist with both hands.
Then bend both wrists down while keeping the fist. Hold for a count of 5.
Straighten both wrists and relax fingers, for a count of 5.
Repeat the exercise (a-f) 10 times
Then let your arms hang loosely at the side and shake them for a few seconds.
* Wrist Curls without Weights: Sit in a chair with your forearm resting on your thigh (or on a table) keeping your palm up or palm down. Turn your wrist up about 2 to 3 inches and then slowly lower it down. Repeat 20 times.
* Shrugs
Stand with your arms by your sides. Lift your shoulders up to your ears and hold for 1 second. Then pull your shoulders back pinching your shoulder blades together. Hold for 1 second. Relax your shoulders. Do this 20 times.
Reference:
* Carpal Tunnel Syndrome in Patients with Diabetic Polyneuropathy : Bruce A Perkins, FRCPC; David Olaleye, PHd; Vera Bril, MD FRCPC
* Dr. Housang Seradge at the University of Oklahoma Orthopaedic & Reconstructive Research Foundation:
(http://ortho-ok.com.orrf.ORRF_CARPAL_TUNNEL_PREVENTION.html)
* Carpal Tunnel Syndrome Exercises – En Espanol
(http://www.medicinenet.com/carpal_tunnel_syndrome/article.html)
* [Carpal tunnel syndrome in diabetes mellitus].[Article in German]Bahrmann A, Zieschang T, Neumann T, Hein G, Oster P.
|
Bookmark this post:
|
|
Friday, November 18, 2011
Exercises to Strengthen Muscles of the Feet
S.Bamila
M.V. Centre for Diabetic Foot Care, Podiatry, Research & Management
This is a set of six foot exercises to be done while you are sitting on a high seat with feet not touching the ground.
1. Bend toes down. Try to keep toes straight. You can use your hand to help position the toes or get someone to help you.
2. Raise ankle up, but keep toes down.
3. Relax the toes.
4. Flex toes down and at the same time flex ankle down. Feel a squeeze in the arch.
5 . While keeping toes flexed, move the front of the foot inward (inversion)
6. Then move the front of the foot outward (eversion). Relax.
Repeat steps 1-6
DO these FOOT EXERCISES with feet on the ground.
1. Exercise position: Sit in a chair with feet flat on the floor. Raise toes off the floor several times. Keep the ball of the foot on the floor. This exercise is important for walking and helps to keep up the normal range of movement of the toe joints.
2. Exercise position: Sit in a chair with feet flat on the floor. Slide the foot back under the chair. Raise the heel, while keeping the ball of the foot and the toes on the floor. This exercise stretches tight muscles under the foot and maintains normal range of motion of the toe joints.
3. Exercise position: Sit in a chair, with feet flat on floor. Keeping the feet and toes flat on the floor, press the toes into the floor. Keep them as straight as possible. Do not allow them to curl. This strengthens the small muscles of the toes.
4. Exercise position: Sit in a chair, with feet hanging loosely. Spread the toes far apart then squeeze together as tightly as possible. After some practice, you can put a wide rubber band around your toes and spread them against resistance, further increasing strength of the small muscles. 
5. Exercise position: Sit in a chair, with feet flat on the edge of a bath towel or newspaper. Curl the toes and draw the towel/ newspaper under the foot. As you get stronger, add a weight to the other end of the towel/ newspaper. This exercise strengthens intrinsic muscles.
6. Exercise position: Sit in a chair. Place a marble on the floor, and pick it up with your toes. This exercise strengthens the small muscles of the toes.
7. Exercise position: While standing, hold lightly onto a counter top or sturdy chair for balance. Rise up onto the tips of the toes, then rock back onto the heels, lifting the toes off the floor at the same time. Do this several times. This can also be done while sitting.
This exercise improves balance and leg strength when done standing and increases foot and ankle movements and strength of the muscle.
It is important to keep this muscle strong and your ankle flexible so that you can pick up your toes when you walk, and avoid tripping.
8. Exercise position: Sit in a chair. Straighten one knee and bend the ankle. Point the toes toward the knee and feel the stretch of the calf muscle . Repeat 4 times on each leg, alternating legs. This exercise prevents cramps in the lower leg.
9. Exercise position: Sit in a chair. Move your feet as if you are writing alphabets in the air.
|
Bookmark this post:
|
|
Wednesday, November 9, 2011
World Diabetes Day

Mrs. Sheela Paul
World diabetes day is celebrated on 14th of November of every year around the world, to raise primary global awareness among people about diabetes. It was introduced in 1991 by the International Diabetes Federation and the World Health Organization in response to the alarming rise of diabetes around the world. World Diabetes Day is a campaign that features a new theme chosen by the International Diabetes Federation each year to address issues facing the global diabetes community. While the campaigns last the whole year, the day itself marks the birthday of Frederick Banting who, along with Charles Best, first conceived the idea which led to the discovery of insulin in 1922
Each year, World Diabetes Day is centered on a theme related to diabetes. Topics covered have included diabetes and human rights, diabetes and lifestyle, diabetes and obesity, diabetes in the disadvantaged and the vulnerable, and diabetes in children and adolescents.
For 2009–2013, the theme is Diabetes Education and Prevention.
World Diabetes day is celebrated worldwide in more than 160 countries, all member States of the United Nations, healthcare professionals and many more.
The logo of the World Diabetes day is represented by a blue circle. This blue circle resembles to the global symbol of diabetes and signifies the unity of the global diabetes community in response to the diabetes pandemic.
In large towns and metro cities, most of the people don’t eat healthy food, and also doing very less exercise, that may be the major reason of this disease. By taking proper healthy diet and regular exercise will help to control Diabetes. But frankly telling there is no permanent cure for Diabetes.

There are lots and lots of activities organized on this day. These activities includes Radio and Television Programs, Poster Awareness Campaigns, Social Exhibitions, Lightings at monuments and homes, Press Conferences, Diabetes Workshops, Screening of Documentaries films on Diabetes, Public Meeting to distribute information to general public, Sports events or Cycle Racing, Special events or activities for children and Newspaper or Magazine Articles. Every Year, this World Diabetes Day activity is center around the topics that related to diabetes.
About 285 million people from all over the world are affected by Diabetes and it is also expected that this figure may rise up to 435 million by year 2030 if no action implement to stop Diabetes. Generally, it is believed that only aged people suffer from Diabetes but several studies and instances proved that the disease does not limited to any age, anyone can be affected by Diabetes.
World Diabetes day is a call to all those who are responsible for Diabetes care and can contribute to control it. For a diabetic patient, this is a message for empowerment education so that he can follow proper ways whether diet food or exercises to improve his health. For Doctors or healthcare professionals this is an alert to improve knowledge so that proper cure can be discovered. For government, it is a time to implement proper policies for prevention of diabetes. And for general public this is a call to be alert against Diabetes and understand the serious impact of diabetes. 

However, if you have diabetes, you also can live a normal, productive life. It's important, though, to monitor your diabetes and be active in taking good care of your health by recognising its symptoms properly at the right time. In last, we would like to add ‘Prevention is better than cure’, as there is no need for any cure if we take proper steps and stay away from these kind of diseases through proper prevention.
|
Bookmark this post:
|
|
Tuesday, November 1, 2011
Socio-Cultural Changes and Diabetes
With India being dubbed the ‘Diabetes capital of the world’ it is necessary to understand the reasons that contribute to it, the changes it brings about in an individual’s life and explore ways to tackle them.
Great social and cultural changes have taken place in our society. The relatively simple and austere life style of our forefathers has given way to a lavish one where there is no limit to what money can buy.
People don’t exert themselves. The benefits of labour- saving devices and automated transport have forced people to reduce their levels of physical activity.
Easy access to mass produced refined high calorie foods which are affordable and heavily advertised have resulted in an increase in food consumption which is far more than what the body needs.
The fast pace of modern life ,changing values , longer working hours, and changes in family responsibilities have adversely influenced eating patterns and time spent on recreation and outside activities.
As a result, life style diseases such as diabetes, cardiac conditions, obesity, and circulatory problems are fast approaching epidemic proportions.
The three most important risk factors for Type 2 diabetes are sedentary life style,

poor dietary habits 

and , the ensuing changes in body composition.
These are risks that can be avoided.
A person with diabetes has to get used to changes in lifestyle, has to adhere strictly to the treatment and also has to be prepared for the onset of diabetes related complications. So, prevention is better than cure.
Changes in the life of a T2DM
High blood glucose levels and poor control can result in medical complications such as cardio-vascular diseases, retinopathy, neuropathy, and nephropathy.
Apart from that, it can influence many areas of a person’s life – changes in the daily routine due to activities focused on adequate blood glucose control, ability to work, impact on other members of the family, quality of life, sexual functioning and so on.
Diet and exercise, blood glucose monitoring, timing and dosage of oral medication or insulin, hypo management and prevention, foot care, sick day management, visits to the doctor,
medical checks and education activities
– all these have to be integrated into the normal day-to-day activities of people with diabetes.
In addition, they may have to tackle unexpected crises.
In most cases, Type 2 diabetes shows up in middle adulthood. This is a time when behavior patterns of an individual are firmly set and changes for self- care have to be made to improve blood glucose control and to slow down the advancement of diabetic complications. It may require a lot of effort to make the necessary changes. It is difficult to make changes to food habits and even more challenging to maintain them.
During the time before complications set in or during the early period of complications, many people do not show symptoms. Unpleasant symptoms such as slow healing wounds or ulcers, thickening and narrowing of arteries, tingling or burning sensation in hands, legs and feet, protein in urine, or poor vision are usually followed by an awareness and fear of the seriousness of the disease . When they are absent, the patient is not motivated enough to make the necessary lifestyle changes. In short, they treat diabetes quite lightly.
Diabetes - related emotional distress
People with diabetes often experience emotional distress while living with diabetes and the effect of its complications. Many are afraid of living with diabetes and might get depressed at the thought of it. The cost of treatment is also a source of worry. Most often they worry about the future and the possibility of diabetic complications. They are constantly concerned about food and eating and feel deprived when they cannot eat what others can. They are also concerned if changes in their moods/feelings were related to diabetes.
A short tool, the PAID (Problem Areas in Diabetes ) Scale, (Psychosocial issues and Type 2 Diabetes – Gary W Welch, Katie Weinger and Alan M Jacobson), can be used to check high emotional distress related to life with diabetes. It consists of a set of twenty questions to be answered on a 5- point scale ranging between ‘not a problem’ to ‘a serious problem’.
A score above 50 shows a high level of emotional distress. Questions which score 4 on the scale indicate areas the patient finds difficult and may be’ hot- spots’ which are causing heightened emotional stress and might need professional attention.
Good listening is good for diabetes management. 
Talking to people with diabetes about how they feel , and about the practical barriers they face for good diabetic self care is very important. Good listening increases the therapeutic bond and is good for diabetes management. Giving the patient a chance to talk about how he feels about his condition; being open, supportive and non-judgmental; using open- ended questions where the patient can provide information about feelings, instead of closed questions with yes/no answers; not interrupting or sharing personal views while the patient is talking; being aware of the patient’s body language(tone of voice, facial expressions use of hands, body posture, pauses, hesitations during difficult moments); maintaining good eye contact; using small encouraging body signals- nods, yes/no/ummm… are of great value to both physician and patient.
Briefly summarizing what you have heard, and checking with the patient whether what you heard is accurate at the end of the conversation is also essential.
A patient will feel less stressed once he has expressed his fears and hopes and will be motivated to make the necessary behavioural changes.
The greatest challenge in tackling T2DM is to focus on social and cultural changes and reverse the current trend through sensible, preventive strategies.
To control this growing problem , we need to prevent obesity as early in life as is possible , and this can only be done through a strong interaction between policy makers, medical fraternity and the individual.
Reference:
Gary W Welch; Katie Weinger; and Alan M Jacobson. "Psychosocial issues and Type 2 Diabetes." In Textbook of Type 2 Diabetes, Edited by Barry J Goldstein and Dirk Muller-Weiland. London, Martin Dunitz : 65-76; 2003.
|
Bookmark this post:
|
|
Monday, October 24, 2011
Sweet Deepavali for diabetic and their family
- Nutrition Department
Deepavali is a major Indian festival celebrated by Hindus, Jains and Sikhs across the globe as the “Festival of Light,” where the lights or lamps signify victory of good over the evil within every human being. This festival is celebrated with joy and charm that is unmatched in celebration with any other festival.
Deepavali, as it is popularly called, is the festival of lights as “Deepam” mean lamp and Oli light. Both words when combined forms the word Deepavali. It symbolizes the victory of righteousness and the lifting of spiritual darkness. The word Deepavali literally means rows of clay lamps. It is celebrated on the New Moon day of the dark fortnight during October-November. It is also associated with the return to Ayodhya of Lord Rama, his wife Sita and His brother Lakshmana after their fourteen-year sojourn in the forests. The day also marks the coronation of Lord Rama.
Lord Krishna waged a fierce battle and killed the demon. When the evil Naraka was finally killed by Bhagwan Krishna and Satyabhaama, he begged pitifully for mercy; thus, upon his entreaties, Bhudevi declared that his death should not be a day of mourning but an occasion to celebrate and rejoice. Since then, Deepavali is celebrated every year with lots of fun and frolic and fireworks.
Deepavali is not just a festival for worshipping Goddess Lakshmi, eating sweets, wearing new clothes or lighting ghee lamps. There is a great secret significance of this festival and understanding it can enable one to celebrate the festival in the best possible manner. Diyas, candles and crackers add light to the festival, rangoli add colours and sweets and other delicious savouries add flavour to this festival. 
You relish the delicacies but later on regret. Heart burns, gastric troubles, indigestion, high blood pressure, elevated blood glucose levels, weight gain…all are some of the after effects of Diwali celebrations. These problems may tarnish your festival spree especially those who are diabetic.
To keep blood glucose level normal, even after eating sweets, he/she as to substitute small portions of sweet for other carbohydrates containing foods in the meals and snacks. For example, if a person wants to have sweet in a meal, then he should replace any other carbohydrate content of his meal. The total amount of carbohydrate ingested during the meal will remain the same.
Though, the sweets does not provide any important vitamins and minerals, they may be high in fats and calories but while including them in the meal plan one must make sure that it provides necessary nutrients.
Person, who likes sweets & desserts, can try these tips
(a) Eat a small serving of the favorite dessert, instead of something common.
(b) Satisfy your sweet tooth with fresh or dry fruits.
(c) Share desserts with your friend or family member.
(d) Reduce the amount of sugar or fat in your favorite recipes.
(e) Choose low calorie and low fat desserts.
So, enjoy this Diwali with the scrumptious delicacies without cutting out anything from your menu. Just a little change in the preparation method and you get the same but much healthier recipe to relish on. Here are some low-calorie yummy but healthy recipes...
FRUIT PUDDING
INGREDIENTS:
(Note: You can Serve this for 4)
1. ¼ cup water.
2. 1 heaped teaspoon gelatin
3. ½ cup pineapple tidbits
4. 1 apple, chopped
5. 4 dried apricots, chopped
6. 2 cups curd made from fat-free milk, whisked.
7. A few drops vanilla essence.
METHOD:
1. Heat water in a small pan over low heat. Sprinkle in gelatin and remove from heat. Set aside for about 10 minutes, stirring occasionally till gelatin is dissolved.
2. Place dissolved gelatin, pineapple, apple, apricots, curd and vanilla in a bowl and stir till well mixed. Pour into a wet mould.
3. Refrigerate till set and chilled.
4. Unmould onto a glass dish and decorate with a few fruit pieces.
NUTRITIVE VALUE PER SERVING:
Calories-122
Protein- 5gms
Fat- 2 Gms.
CHO- 21gms
FRUIT&VEG PEEL HALWA
Serving size: 4 cups
Ingredients
* Apple peel, ½ cup
* Mango peel, ½ cup
* Carrot peel, ½ cup
* Beetroot peel, ½ cup
* Tomato peel, ½ cup
* Milk, 200 ml
* Wheat flour, 2 tbsp
* Ghee, 2 tsp
* Almonds, 25gm
* Sugar free, as required
Directions
1. Grind all the peel together in the mixer with 2 spoons of milk.
2. Heat kadai and add remaining milk and bring into boil.
3. Add ground peel mixture into boiling milk and mix well.
4. Add wheat flour and ghee little by little and cook until the mixture leaves side of the kadai.
5. Turn off the flame and mix the sweetener as required.
6. Garnish with chopped almonds and serve cold.
Nutritive values per serving:
1 cup= 150ml
Note:
1cup of dessert can be substituted for 1 cup of rice or 1 chapatti or 50-100g of fruit. But not in regular basis has too much of sweetener is not recommended.
Apart from this, stick to your meal timings and food quantities. Don’t increase your medication without your doctor’s consent. Continue your exercise routine as usual. Finally don’t forget to check your blood sugars and keep them within limits at all times.
Remember, you can have a sweet life without sweets!!!
|
Bookmark this post:
|
|






